It’s a dynamic and exciting time in the field of AI as advancements in research are being translated into products that bring real benefits to people. This is evident in the case of large language models, such as the Language Model for Dialogue Applications (LaMDA), which was introduced two years ago, showcasing the latest language and conversational capabilities.
Google’s foray into the field of conversational AI has been marked by the development of an experimental conversational AI service powered by LaMDA. This innovative service, known as Bard, holds the promise of transforming the way we interact with technology.
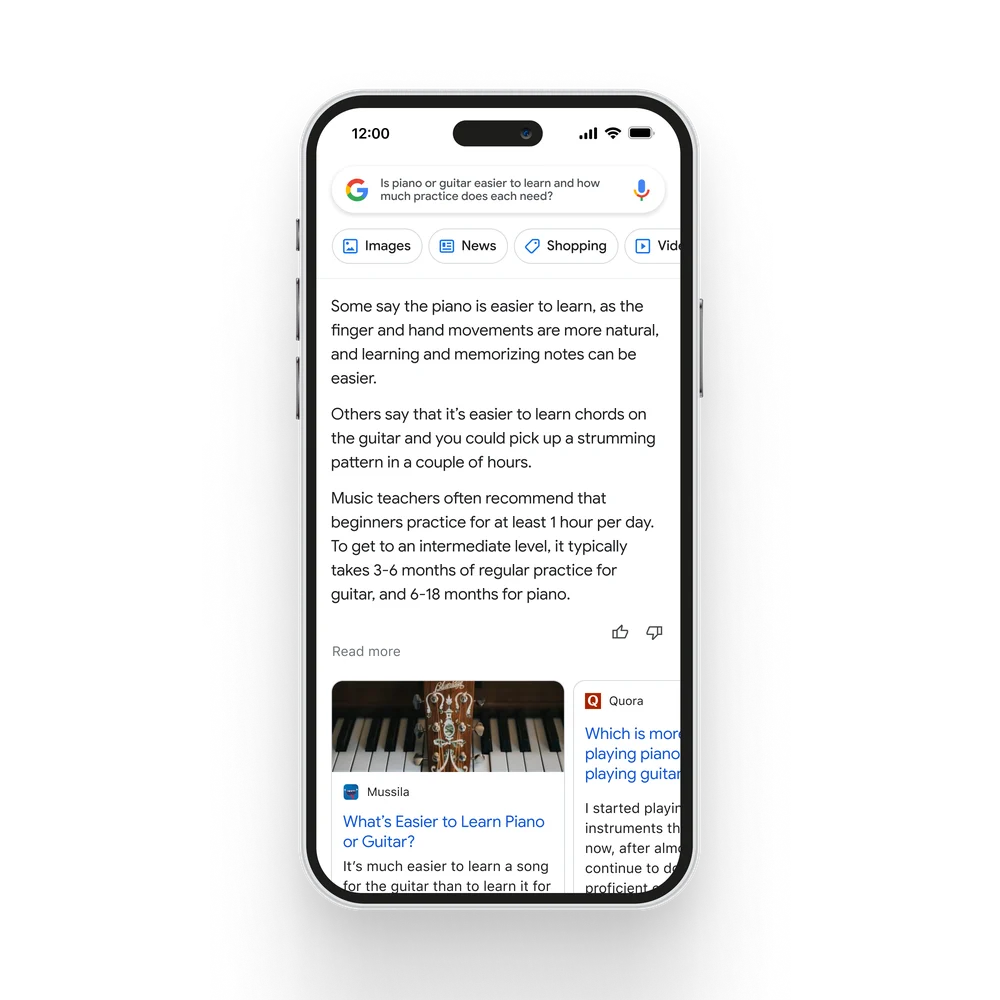
Bard combines the vast wealth of knowledge in the world with the power, intelligence, and imagination of large language models. By utilizing information available on the web, Bard provides fresh and high-quality responses, serving as a platform for creativity and sparking curiosity.
To make the most of these advances, Google is making it easy, safe, and scalable for others to build on top of their best models. In the coming months, Google will be onboarding individual developers, creators, and enterprises, allowing them to try the Generative Language API, which is initially powered by LaMDA, with a range of models to follow. The company intends to create a suite of tools and APIs to make it easier for others to build innovative AI applications.
The goal of Bard is to merge the vast amount of information in the world with the capability, intelligence, and imagination of large language models. It utilizes information available on the web to generate new and accurate responses. Bard can serve as a platform for creativity and a starting point for inquisitiveness, allowing individuals to easily explain complex concepts, such as new discoveries from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, to a child or to gain knowledge about the best football strikers and related training drills.
The initial release of Bard will feature a lightweight version of the Language Model for Dialogue Applications (LaMDA). This smaller model requires less computing resources, enabling scalability to a larger number of users and providing opportunities for more feedback. The external feedback, along with internal testing, will be used to ensure that Bard’s responses meet high standards for quality, safety, and relevance to real-world information. This phase of testing is expected to further enhance the quality and speed of Bard and provide opportunities for continued learning and improvement.
The company believes that it is important to make it easy, safe, and scalable for others to take advantage of advancements in AI technology. To that end, the company will begin onboarding individual developers, creators, and enterprises next month to try its Generative Language API, initially powered by LaMDA with a range of other models to follow. Over time, the company intends to create a range of tools and APIs to simplify the process of building innovative applications with AI.
Access to the necessary computing power is a critical aspect for startups in the AI space, and the company is working to address this through its partnerships with Google Cloud, Cohere, C3.ai, and Anthropic, which was announced last week. These partnerships aim to help scale AI efforts and build reliable and trustworthy AI systems. In conclusion, Google has evolved from being known for providing quick and factual answers to questions to being a source of deeper insights and understanding. The introduction of Bard is an exciting development in the field of conversational AI, and Google’s commitment to making AI accessible to everyone makes it a thrilling time to be involved in the industry.
Discover more from SNAP TASTE
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.


